中国电子科技集团公司 第二十六研究所,重庆 400060
该文研制了一种高性能温补型薄膜体声波谐振(TC-FBAR)滤波器。采用COMSOL软件对高性能温补型结构的谐振器进行建模和仿真,在常规一维Mason等效电路模型的基础上进行修正,再在ADS中对滤波器进行仿真优化设计,得到阶梯型结构的TC-FBAR滤波器。采用空腔型结构并制备出温补型FBAR滤波器芯片,同时在常规TC-FBAR基础上制备空气桥和凸起层结构,得到双空气桥结构的高性能TC-FBAR滤波器。测试结果表明,滤波器的中心频率为2.43 GHz,最小插损为1.02 dB,1 dB带宽为70.5 MHz,频率温度系数为1.82×10-6/℃。
温补型薄膜体声波谐振器(TC-FBAR) 滤波器 温补层 频率温度系数(TCF) temperature compensation thin-film bulk acoustic r filter temperature compensation layer frequency temperature coefficient(TCF)
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China
5 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
The dense quantum entanglement distribution is the basis for practical quantum communication, quantum networks and distributed quantum computation. To make entanglement distribution processes stable enough for practical and large-scale applications, it is necessary to perform them with the integrated pattern. Here, we first integrate a dense wavelength-division demultiplexing system and unbalanced Mach-Zehnder interferometers on one large-scale photonic chip and demonstrate the multi-channel wavelength multiplexing entanglement distribution among distributed photonic chips. Specifically, we use one chip as a sender to produce high-performance and wideband quantum photon pairs, which are then sent to two receiver chips through 1-km standard optical fibers. The receiver chip includes a dense wavelength-division demultiplexing system and unbalanced Mach-Zehnder interferometers and realizes multi-wavelength-channel energy-time entanglement generation and analysis. High quantum interference visibilities prove the effectiveness of the multi-chip system. Our work paves the way for practical entanglement-based quantum key distribution and quantum networks.

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Chongqing United Microelectronics Center (CUMEC), Chongqing 401332, China
4 Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
5 e-mail: wwq@opt.ac.cn
6 e-mail: wfuzhang@opt.ac.cn
A high-quality optical microcavity can enhance optical nonlinear effects by resonant recirculation, which provides a reliable platform for nonlinear optics research. When a soliton microcomb and a probe optical field are coexisting in a micro-resonator, a concomitant microcomb (CMC) induced by cross-phase modulation (XPM) will be formed synchronously. Here, we characterize the CMC comprehensively in a micro-resonator through theory, numerical simulation, and experimental verification. It is found that the CMCs spectra are modulated due to resonant radiation (RR) resulting from the interaction of dispersion and XPM effects. The group velocity dispersion induces symmetric RRs on the CMC, which leads to a symmetric spectral envelope and a dual-peak pulse in frequency and temporal domains, respectively, while the group velocity mismatch breaks the symmetry of RRs and leads to asymmetric spectral and temporal profiles. When the group velocity is linearly varying with frequency, two RR frequencies are hyperbolically distributed about the pump, and the probe light acts as one of the asymptotic lines. Our results enrich the CMC dynamics and guide microcomb design and applications such as spectral extension and dark pulse generation.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(6): 1075
重庆市信息通信咨询设计院有限公司,重庆 400041
针对大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)系统中线性最小均方误差(MMSE)信号检测算法复杂的高维矩阵求逆难以用于实际工程的问题,文章基于矩阵分块思想并结合Neumann级数展开算法,提出了一种低复杂度的混合迭代算法。利用MMSE算法中加权矩阵逆矩阵的Neumann级数二阶展开作为其分块矩阵求逆的迭代初始值,可以有效提高算法收敛速度。仿真结果表明,该方法能以较少迭代次数逼近传统MMSE算法较优检测性能,并降低计算复杂度。
信号检测 大规模多输入多输出 混合迭代 矩阵分块 Neumann级数展开 signal detection massive MIMO hybrid iteration matrix block Neumann series expansion
三峡大学材料与化工学院,无机非金属晶态与能源转换材料重点实验室,宜昌 443002
采用溶胶-凝胶旋涂法在玻璃衬底上沉积纳米结构Ti、Ga共掺ZnO薄膜(TGZO,Ga掺杂量为1.0%(原子分数,下同)),用X射线衍射仪(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、分光光度计(UV-Vis)、四探针测试仪、霍尔效应测试仪研究了Ti含量对TGZO薄膜的物相组成、表面形貌、电学和光学性能的影响。结果表明:所有TGZO薄膜均表现出六方纤锌矿的多晶结构,并具有(002)择优取向生长,在380~780 nm波长范围内具有良好的透射率(>86%);随着Ti含量的增加,TGZO薄膜的晶粒尺寸和可见光平均透射率均先增加后减小,而光学带隙和电阻率先减小后增加;Ti掺杂量为1.0%时,具有最高的可见光透射率92.82%,最窄的光学带隙3.249 eV,以及最低电阻率2.544×10-3 Ω·cm。
TGZO薄膜 溶胶凝胶法 光电性能 c轴择优取向 高透过率 TGZO thin film sol-gel method photoelectric property c-axis preferred orientation high transmittance
国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
通过引入长锥形增益光纤综合抑制受激布里渊散射和模式不稳定效应,兼顾1030 nm波段信号光放大的高模式不稳定阈值特性,基于全光纤放大器实现了550 W的近衍射极限单频光纤激光输出,整个放大器的斜率效率达80%,最高功率时的光束质量测量值M2约为1.47;系统亮度的进一步提升受限于热致模式不稳定效应。
激光器 高功率光纤激光 单频 受激布里渊散射 模式不稳定
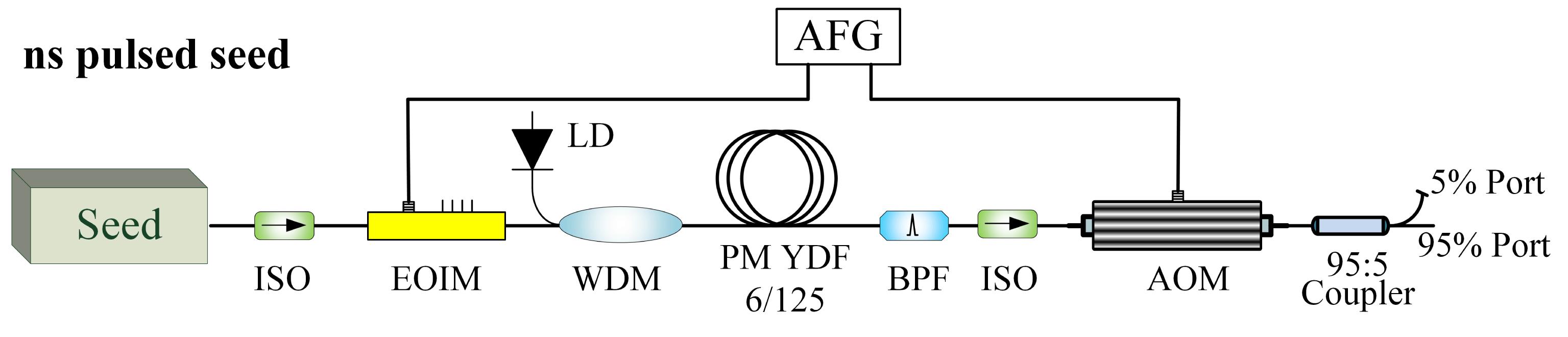
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of High Power Fiber Laser, Changsha 410073, China
An all-fiberized high-average-power narrow linewidth ns pulsed laser with linear polarization is demonstrated. The laser system utilizes a typical master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) configuration. The stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) is effectively suppressed due to the short fiber length and large mode area in the main amplifier, combined with the narrow pulse duration smaller than the phonon lifetime of SBS effect. A maximal output power of 466 W is obtained with a narrow linewidth of

203.6 MHz, and the corresponding slope efficiency is

80.3%. The pulse duration is condensed to be

4 ns after the amplification, corresponding to the peak power of 8.8 kW and the pulse energy of

. Near-diffraction-limited beam quality with an

factor of 1.32 is obtained at the output power of 442 W and the mode instability (MI) is observed at the maximal output power. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest average output power of the all-fiberized narrow linewidth ns pulsed fiber laser with linear polarization and high beam quality, which is a promising source for the nonlinear frequency conversion, laser lidar, and so on.
High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(3): 03000e42

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of High Power Fiber Laser, Changsha 410073, China
3 e-mail: jmxu1988@163.com
In this paper, we propose and experimentally investigate a linearly polarized narrow-linewidth random fiber laser (RFL) operating at 1080 nm and boost the output power to kilowatt level with near-diffraction-limited beam quality using a master oscillation power amplifier. The RFL based on a half-opened cavity, which is composed of a linearly polarized narrow-linewidth fiber Bragg grating and a 500 m piece of polarization-maintained Ge-doped fiber, generates a 0.71 W seed laser with an 88 pm full width at half-maximum (FWHM) linewidth and a 22.5 dB polarization extinction ratio (PER) for power scaling. A two-stage fiber amplifier enhances the seed laser to the maximal 1.01 kW with a PER value of 17 dB and a beam quality of and . No stimulated Brillouin scattering effect is observed at the ultimate power level, and the FWHM linewidth of the amplified random laser broadens linearly as a function of the output power with a coefficient of about . To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a linearly polarized narrow-linewidth RFL with even kilowatt-level near-diffraction-limited output, and further performance scaling is ongoing.
Lasers, distributed-feedback Fibers, polarization-maintaining Linewidth Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Photonics Research
2017, 5(4): 04000350

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of High Power Fiber Laser, Changsha 410073, China
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ryerson University, 350 Victoria St., Toronto, Ontario M5B 2K3, Canada
In this manuscript, we demonstrate high-power, narrow-linewidth linearly polarized fiber laser with excellent beam quality through compact one-stage amplification scheme. By employing a single-mode–multimode–single-mode structure seed laser, a linearly polarized Yb-doped fiber laser with narrow linewidth and high output power is achieved. This laser, when used as a master oscillator, can be capable of suppressing the ASE in the process of power amplification. Thus, only one-stage amplification structure is used to scale up the laser power, and linearly polarized output with a polarization extinction ration of 14 dB, a narrow linewidth of 0.3 nm and an output power of 1018 W are achieved. Moreover, due to the good beam quality of seed laser and the well-designed amplifier stage, the beam quality of the output laser is near-diffraction-limited with $M_{x}^{2}\sim 1.18$ and $M_{y}^{2}\sim 1.24$ at the maximum power, and without mode instability occurring.
fiber amplifier fiber Bragg grating linearly polarization narrow linewidth High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(4): 04000e30
1 南京信息职业技术学院通信学院, 江苏 南京 210023
2 南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院, 江苏 南京210093
基于光注入法布里-珀罗(F-P)激光器的波长选择性放大理论, 设计并实现了一种窄带可调谐的单通带微波光子滤波器(MPF)。通过改变注入锁定参数, 研究了注入锁定参数对中心频率、插入损耗和带外抑制比等性能指标的影响, 以及波长功率放大与腔模红移的关系。实验结果表明, 通过合理调节注入功率比、主从激光器失谐频率和偏置电流, 可以获得带外抑制比为27.9 dB、3 dB带宽为275 MHz和调谐范围为9~32 GHz的MPF。所提结构可以应用于高频、宽带可调谐的滤波选频和光电振荡。
光通信 光学器件 微波光子 滤波器 注入锁定 法布里-珀罗激光器 波长选择性放大 中国激光
2017, 44(10): 1006002





